1.4 The User Interface
Myron consists of several components, each of which has its own
display and provides its own responses to user input. The
![]() .
.
When Myron is started, the first component displayed is the algebra workspace. This is where algebraic expressions are entered, transformations are applied and results are presented. It is also where other program components are initiated.
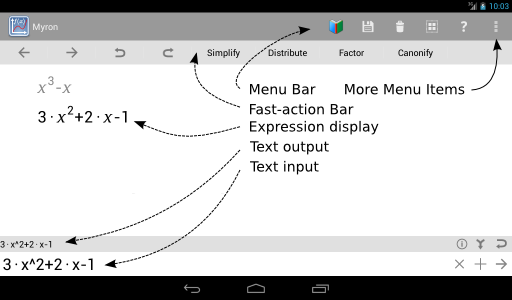
A large number of user-interface controls are visible in the algebra workspace (Figure 1.1). Most of these are buttons that initiate programmed activity when touched or clicked. The buttons are arranged into four groups: the menu bar (across the top), the fast-action bar (below the menu bar), the region to the right of the text-input area (at the bottom) and the region to the right of the text-output area (above the text-input area).
At the right extreme of the menu bar, a button with the icon
 produces a drop-down menu. Some items on the menu produced additional
menus.
produces a drop-down menu. Some items on the menu produced additional
menus.
 On devices with small screens, the menu icon might be a hardware
button.
On devices with small screens, the menu icon might be a hardware
button.
Some buttons and menu items hand control of the display over to other program components. As mentioned above, these have their own user-interface controls. Each component is described in its own section of this guide.
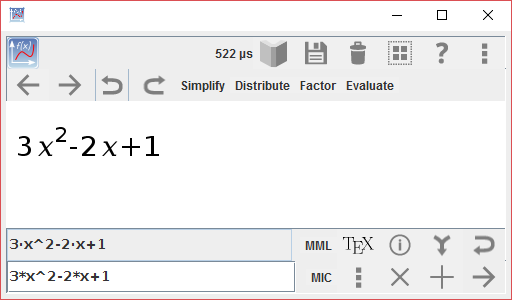
 The desktop version of Myron
(Figure 1.2) has a similar appearance,
but note some additional buttons to the right of the
text-input and text-output areas. These control features of the desktop
version that are different from the Android version. They are described
in §2.11.3.
The desktop version of Myron
(Figure 1.2) has a similar appearance,
but note some additional buttons to the right of the
text-input and text-output areas. These control features of the desktop
version that are different from the Android version. They are described
in §2.11.3.
The Android and desktop displays use touch and mouse inputs in consistent ways.
| Android | Desktop | Action |
| touch | click | select |
| touch and move | move with left button down | drag |
| touch and hold | left button down and hold | long press |
| two-finger pinch | scroll wheel forward with left button down | zoom in |
| two-finger spread | scroll wheel back with left button down | zoom out |